As Artificial Intelligence, especially Large Language Models (LLMs), become more integrated into our daily products and workflows, their immense power is accompanied by significant risks. From generating incorrect or biased information to being manipulated into producing harmful content, the need for control is paramount. This is where AI Guardrails come into play.
Think of guardrails on a mountain road. They don't control your driving, but they provide a critical safety barrier that prevents you from going off a cliff. Similarly, AI guardrails are a set of protective measures that keep AI applications operating within safe, ethical, and predefined boundaries.
This blog will serve as a comprehensive guide to understanding what guardrails are, how they work, their different types, architectural design, and real-world applications.
What are Guardrails?
In the context of AI, Guardrails are a set of technical policies, constraints, and safety mechanisms applied to AI systems – primarily generative AI and LLMs – to ensure their outputs are aligned with desired standards of safety, legality, ethics, and reliability.
They act as a filter and a guide, intercepting both user inputs and AI-generated outputs to:
- Prevent Harmful Content: Block the generation of hate speech, violent extremism, or self-harm instructions.
- Ensure Data Privacy: Detect and redact sensitive information like phone numbers, social security numbers, or personal addresses from being processed or leaked.
- Uphold Legal and Ethical Standards: Prevent copyright infringement, ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA, and mitigate biases.
- Enforce Topic Boundaries: Keep the AI on-topic and prevent it from responding to irrelevant or prohibited subjects (e.g., preventing a customer service bot from discussing politics).
- Guarantee Output Structure: Ensure the AI's response is in a specific format, like valid JSON, a SQL query, or a correctly structured email.
Without guardrails, an AI model is a powerful but untamed engine, capable of producing brilliant results one moment and dangerous nonsense the next.
How Guardrails Work: The Interception and Enforcement Mechanism
Guardrails don't retrain the core AI model. Instead, they operate as an independent layer that wraps around the model, checking inputs and outputs in real-time. The workflow can be broken down into three key stages:
Input Validation & Sanitization:
- Before the user's prompt is sent to the AI model, it passes through the guardrail layer.
- The guardrails analyze the prompt for malicious intent, prompt injection attacks, jailbreaking attempts, or sensitive data.
- If a violation is detected, the guardrail can block the request entirely, sanitize the input by removing sensitive words, or redirect the user.
Output Validation & Filtering:
- After the AI model generates a response, it is intercepted by the guardrail layer before it's sent back to the user.
- The guardrails analyze the output for a wide range of criteria: factual accuracy (via fact-checking against a knowledge base), toxicity, bias, data leaks, and adherence to the desired format.
- If the output fails these checks, the guardrail can filter it out, rewrite it, or trigger a fallback response (e.g., "I cannot answer that question.").
Feedback Loop (Advanced):
- In more sophisticated systems, the results of the guardrail checks can be logged and used to fine-tune the policies or even provide feedback to the underlying AI model for continuous improvement.
This "traffic cop" role ensures that only safe and appropriate content reaches the end-user.
Different Types of Guardrails
Guardrails can be categorized based on their primary function:
Safety & Security Guardrails:
- Jailbreaking Prevention: Detect and block attempts to manipulate the model into ignoring its core instructions.
- Toxicity & Hate Speech Filtering: Identify and block offensive, threatening, or discriminatory language.
- Prompt Injection Defense: Shield the model from attempts to overwrite its system prompt with malicious user instructions.
Privacy & Compliance Guardrails:
- PII (Personally Identifiable Information) Redaction: Automatically detect and mask/remove sensitive data like names, emails, and credit card numbers.
- Compliance Enforcement: Ensure outputs adhere to specific industry regulations (e.g., a financial advisor bot must include necessary disclaimers).
Content & Quality Guardrails:
- Topic Steering: Enforce a defined scope of conversation, preventing the AI from straying into irrelevant or unauthorized areas.
- Fact-Checking & Grounding: Verify the model's claims against a trusted knowledge base (like a vector database) to combat "hallucinations."
- Output Structure Validation: Ensure the response is a valid code snippet, JSON object, or follows a specific template.
Contextual & Operational Guardrails:
- Session Management: Track the conversation history to prevent repetitive loops or manage context windows effectively.
- Rate Limiting: Control the number of requests a user can make to prevent system abuse and manage costs.
Architecture of Guardrails: Where Do They Fit In?
Guardrails are typically implemented as a middleware layer in a larger AI application architecture. Here’s a simplified view of a robust, guarded AI system:
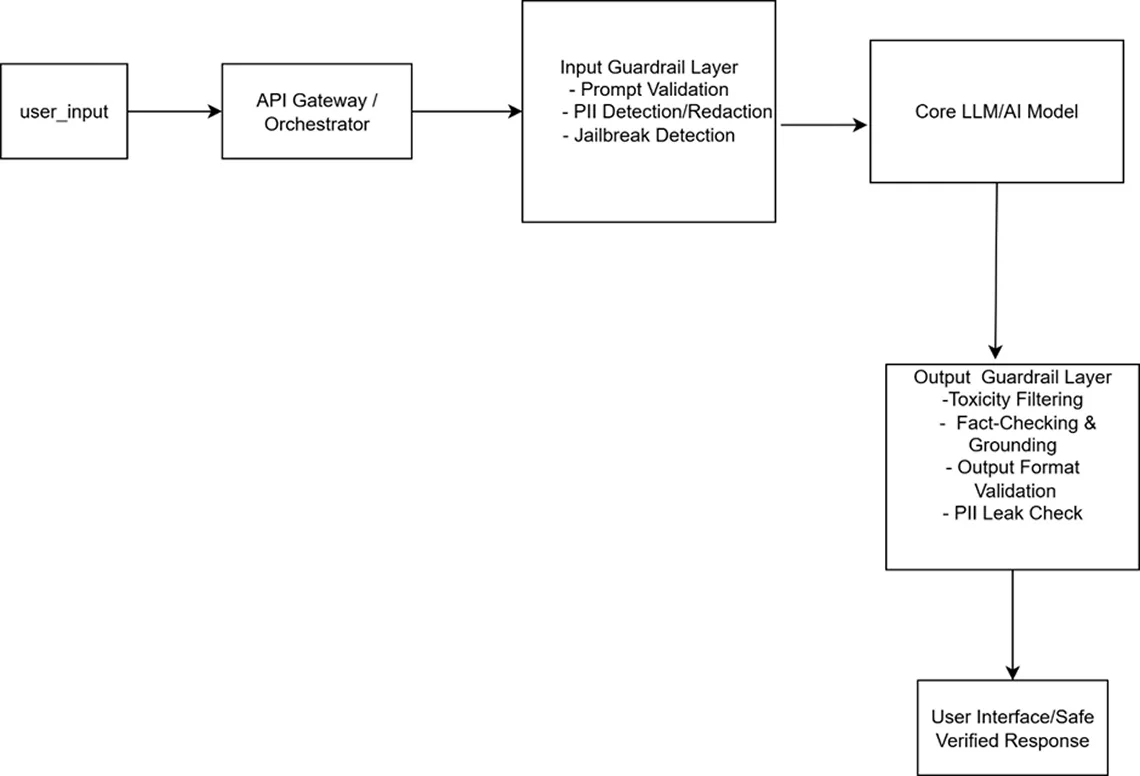
Key Components:
- Orchestrator: The central brain (often using frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex) that manages the flow of data between components.
- Input/Output Guardrail Services: These can be custom-built modules or specialized tools like NVIDIA NeMo Guardrails, Microsoft Guidance, or Azure AI Content Safety.
- Knowledge Base: A trusted source of truth (e.g., a vector database) used for fact-checking and grounding.
- Monitoring & Logging: Essential for tracking guardrail triggers, analyzing failures, and continuously improving the system.
Real-World Use Cases
Guardrails are not a theoretical concept; they are actively being deployed across industries.
Customer Service Chatbots:
- Use Case: A bank uses a chatbot for customer inquiries.
- Guardrails in Action: Prevent the bot from giving financial advice without disclaimers, redact account numbers from the chat log, and block abusive language from users.
Healthcare Assistants:
- Use Case: An AI assistant helps doctors summarize patient notes.
- Guardrails in Action: Automatically redact all Protected Health Information (PHI) to ensure HIPAA compliance before the data is processed or stored.
Content Generation Platforms:
- Use Case: A marketing team uses an AI tool to draft blog posts and social media content.
- Guardrails in Action: Ensure the brand's tone-of-voice is maintained, prevent the generation of plagiarized content, and block the creation of offensive or off-brand messaging.
Internal Enterprise Knowledge Bots:
- Use Case: An AI-powered bot answers employee questions about company policy.
- Guardrails in Action: Restrict the bot's knowledge to only the internal company handbook (topic steering) and ground its answers to prevent hallucinations. It will refuse to answer questions about its own programming or external news.
Code Generation Tools (e.g., GitHub Copilot):
- Use Case: A developer uses an AI to generate code snippets.
- Guardrails in Action: Validate that the output is syntactically correct code, scan for known security vulnerabilities, and prevent the suggestion of code that uses deprecated or unsafe functions.
Final Thoughts: Building Trust, One Guardrail at a Time
AI guardrails are not about limiting potential; they are about enabling responsible innovation. By providing a critical safety and control layer, they allow businesses and developers to harness the transformative power of AI with confidence. As AI models grow more capable, the sophistication of their guardrails will become the defining factor between a risky experiment and a reliable, enterprise-grade application. Implementing a robust guardrail framework is no longer optional - it is the cornerstone of building trustworthy and effective AI systems.
